Earthquake of magnitude 4.3 strikes Afghanistan
Feb 11, 2026
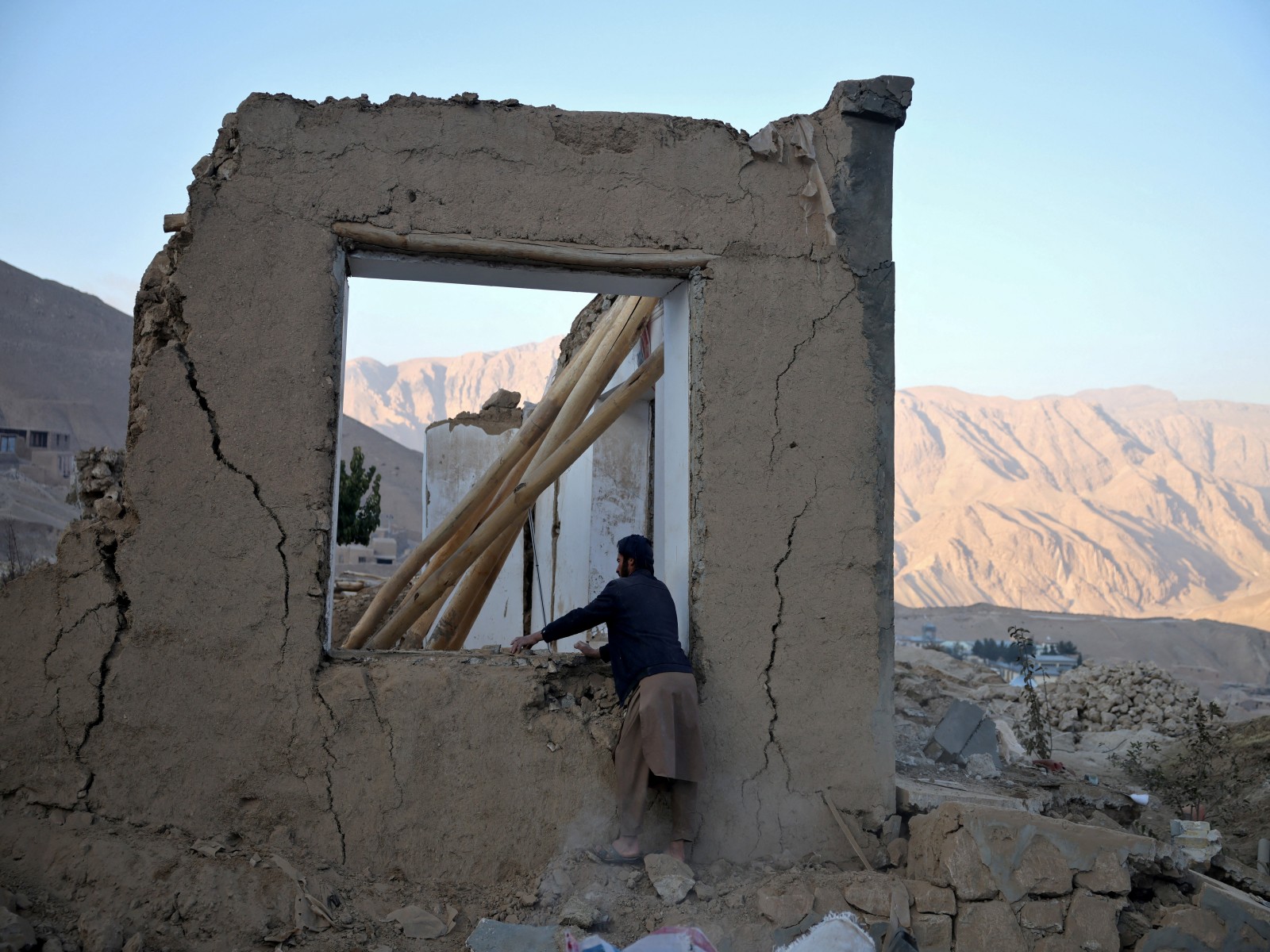

Kabul [Afghanistan], February 12 : An earthquake of magnitude 4.3 struck Afghanistan on Wednesday, a statement by the National Center for Seismology (NCS) said.
The earthquake occurred at a depth of 35km.
In a post on X, the NCS said, "EQ of M: 4.3, On: 12/02/2026 01:40:58 IST, Lat: 37.20 N, Long: 70.31 E, Depth: 35 Km, Location: Afghanistan."
https://x.com/NCS_Earthquake/status/2021681843918307544?s=20
Earlier on February 9, an earthquake of magnitude 4.5 struck the region at a depth of 150km.
In a post on X, the NCS said, "EQ of M: 4.5, On: 09/02/2026 01:11:08 IST, Lat: 36.56 N, Long: 71.47 E, Depth: 150 Km, Location: Afghanistan."
https://x.com/NCS_Earthquake/status/2020586015426261020?s=20
On February 8, another earthquake of magnitude 4.3 struck the region at a depth of 122km.
In a post on X, the NCS said, "EQ of M: 4.3, On: 08/02/2026 21:03:00 IST, Lat: 36.11 N, Long: 70.42 E, Depth: 122 Km, Location: Afghanistan."
https://x.com/NCS_Earthquake/status/2020524547926380732?s=20
On the same day, an earthquake of magnitude 4.4 struck the region at a depth of 80km.
In a post on X, the NCS said, "EQ of M: 4.4, On: 08/02/2026 10:50:45 IST, Lat: 36.32 N, Long: 71.50 E, Depth: 80 Km, Location: Afghanistan."
https://x.com/NCS_Earthquake/status/2020371524444909759?s=20
Afghanistan frequently experiences earthquakes, particularly in the Hindu Kush region, which lies in a highly active seismic zone, according to the Red Cross.
Afghanistan's vulnerability to earthquakes is linked to its location along the collision zone between the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates. A major fault line also passes through parts of the country, including the Herat region.
The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA) notes that Afghanistan remains extremely vulnerable to natural disasters, including earthquakes, landslides and seasonal flooding. Repeated tremors worsen the situation for communities already struggling with decades of conflict and limited development, leaving them with minimal resilience to withstand multiple shocks.